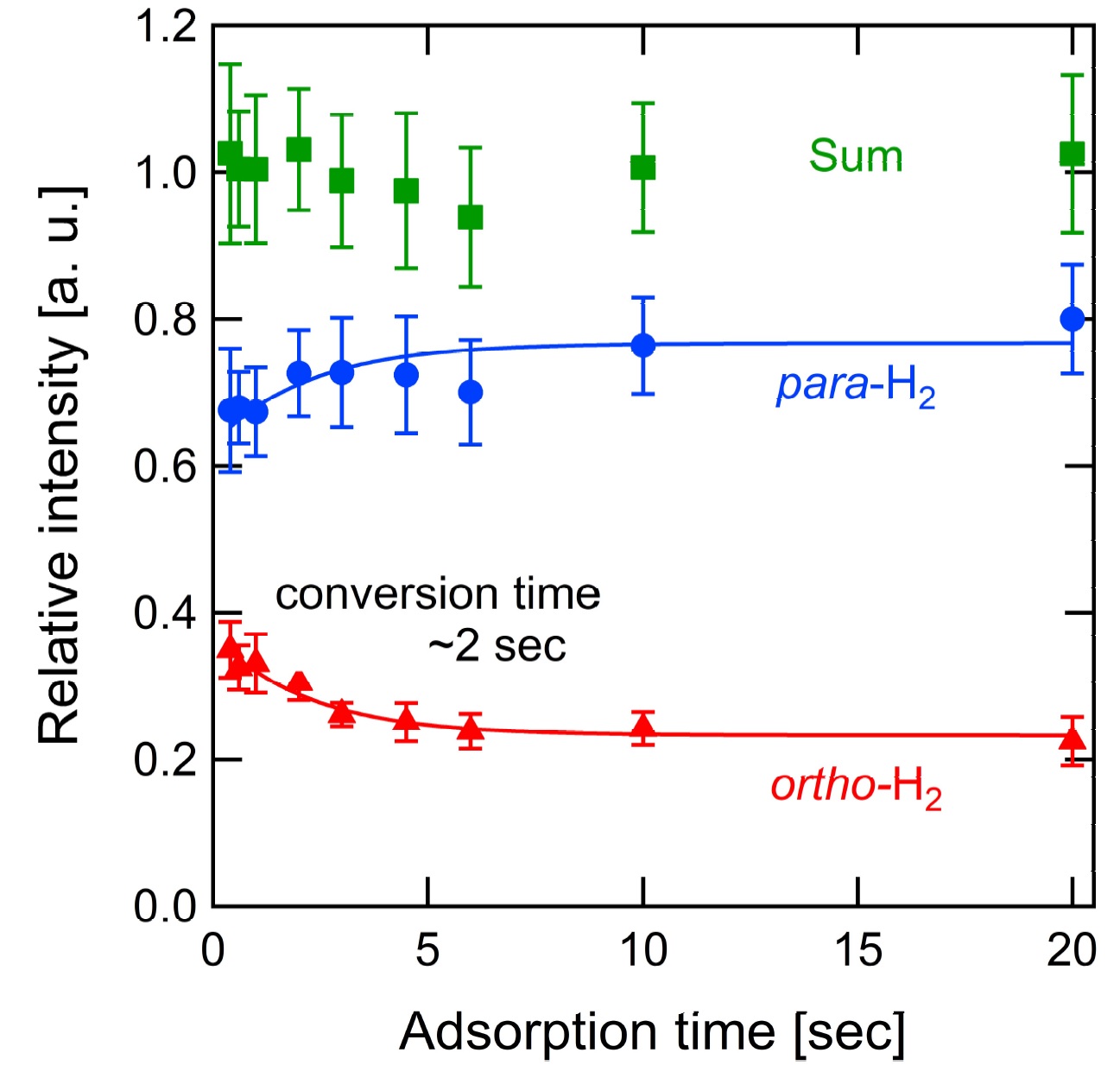
Demonstration of fast ortho-para conversion of H2 on surface
With a combination technique of molecular beam and two lasers, we succeeded to measure a ortho-para conversion time of molecularly chemisorbed H2 on a Pd surface. The conversion time is 2–3 orders of magnitude smaller than those reported for physisorption systems.
H. Ueta et al., Phys. Rev. B 102, 121407(R) (2020).
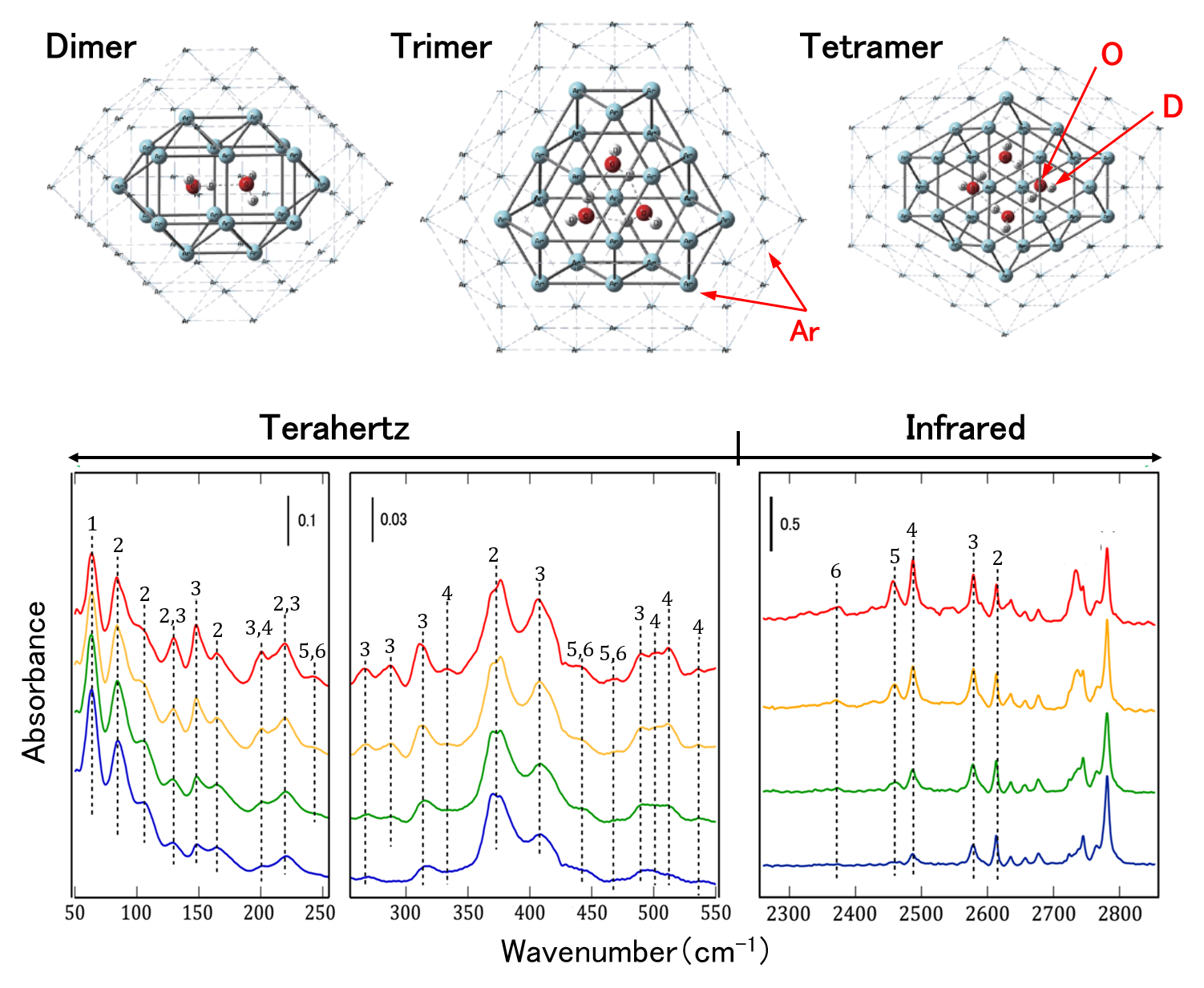
Determination of intermolecular vibrational modes in deuterated water nanoclusters
By employing terahertz and infrared absorption spectroscopy in an ultrahigh vacuum as well as ab initio vibrational calculation, we revealed the intermolecular vibrational modes in the dimer, trimer, and tetramer of deuterated water. This achievement is helpful to precise determination of the hydrogen-bond potential and evaluation of the clustering effect on the atmospheric absorption of solar radiation.
K. Yamakawa et al., J. Chem. Phys. 152, 174310 (2020).
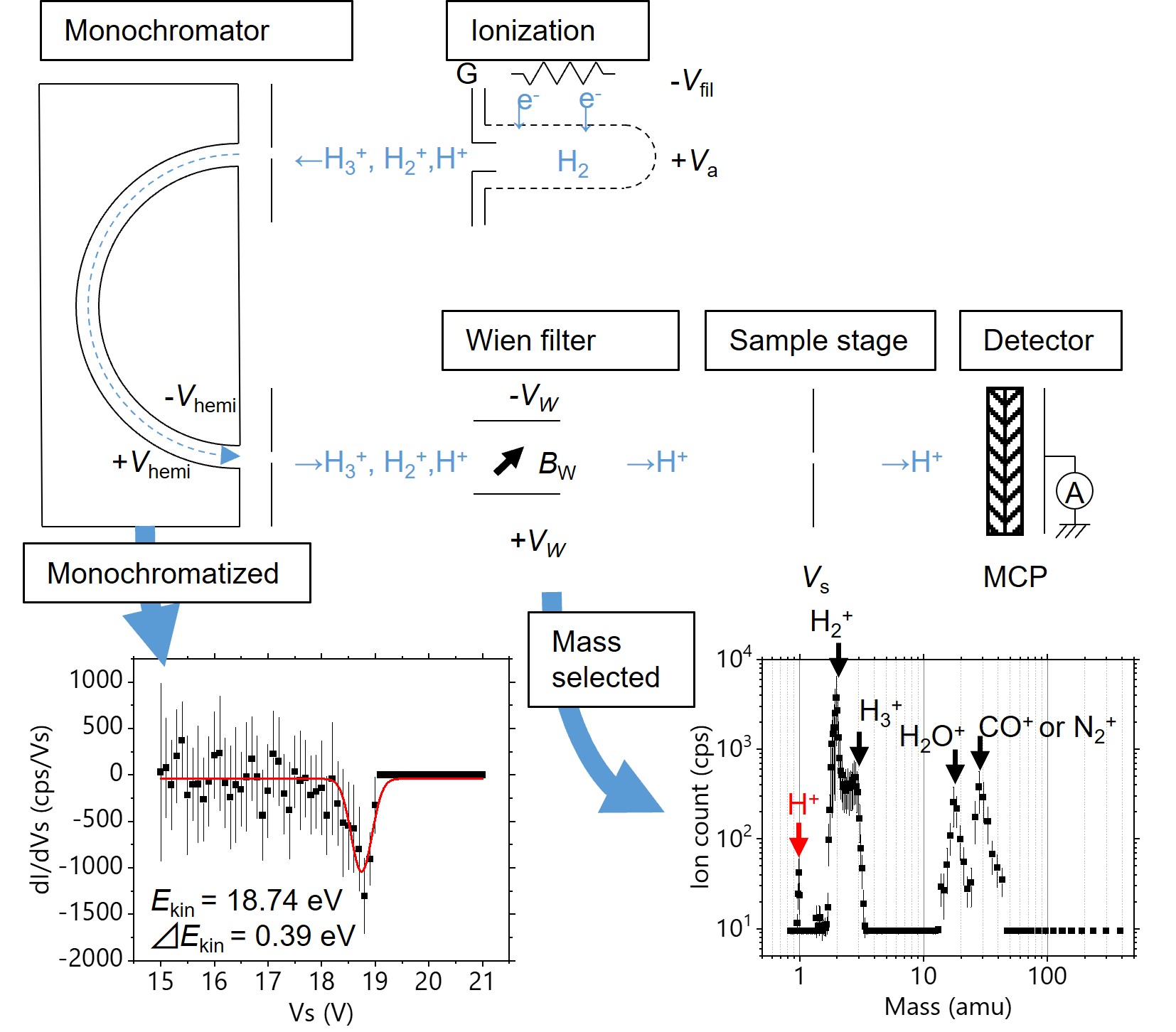
Development of Ultraslow, Monochromatic, and Mass-selected Ion Source
We developed an ultraslow, monochromatic, and mass-selected ion source using hemispherical analyzer and Wien filter toward the measurement of the proton permeability of graphene.
T. Terasawa et al., e-J. Surf. Sci. Nanotech. (2022), in press.
Development of hydrogen isotope separation electrocatalysts by quantum tunneling effect of two dimensional materials
We fabricated heterogeneous electrode with layered structures consisting of palladium and graphene layers (PdGr) for polymer electrolyte membrane electrochemical hydrogen pumping (PEM-ECHP). Electrochemical and theoretical analyses demonstrated that the PdGr electrode exhibits high hydrogen/deuterium (H/D) separation ability due to contribution of quantum tunneling effect of the hydrogen isotope ions through the graphene. The findings would serve as a novel economical methodology of efficient hydrogen isotope enrichment.
S. Yasuda et al., submitted.
Direct growth of germanene at interfaces between van der Waals materials and Ag (111)
We have succeeded in growing germanene, which is Ge analogous of graphene, directly at the solid interface by using Ge segregation from a Ag(111) thin film. We have shown for the first time that germanene can exist stably at the solid interface without being oxidized even in air. The present study also shows that germanene is not formed at the interface between Ag and Al2O3, which is a common oxide, while the Ag/van der Waals material (graphene, hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN)) interface is necessary for germanene synthesis. This is probably due to the low reactivity of the van der Waals material interface, which does not inhibit the germanene formation process at the Ag(111) interface.
S. Suzuki et al., Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2007038 (2021).
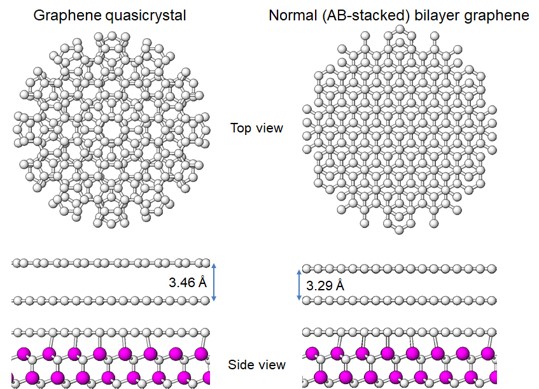
Atomic arrangements of graphene quasicrystal
We succeeded in revealing the atomic arrangements of "graphene quasicrystal", in which two graphene layers are stacked with the twist angle of 30°. As a result, we found that the interlayer spacing in graphene quasicrystal is larger than that of the normal AB-stacked one.
Y. Fukaya et al., Phys. Rev. B 104, L180202 (2021).
Fabrication of low-dimensional nanostructures using surface properties
Nanodots and nanoribbons have been successfully fabricated by utilizing the unique arrangement of atoms and molecules at the surface. Based on these fabrication techniques, we are developing new materials.
M. Yano et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 57, 06HD04 (2018).
Structure of a hydrogen-related paramagnetic defect in SrTiO3
While excess electrons introduced with hydrogen into SrTiO3 are mostly doped into its conduction band and cause metallic conductivity, some of them contrastingly show enigmatic localized behavior. With the use of positive muons as a radioactive hydrogen isotope, we revealed that the excess electron can be trapped at the Ti site adjacent to an interstitially implanted muon to form a muonic analogue of a paramagnetic H+-Ti3+ complex.
T. U. Ito et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 115, 192103 (2019), e-J. Surf. Sci. Nanotech. (2022), in press.
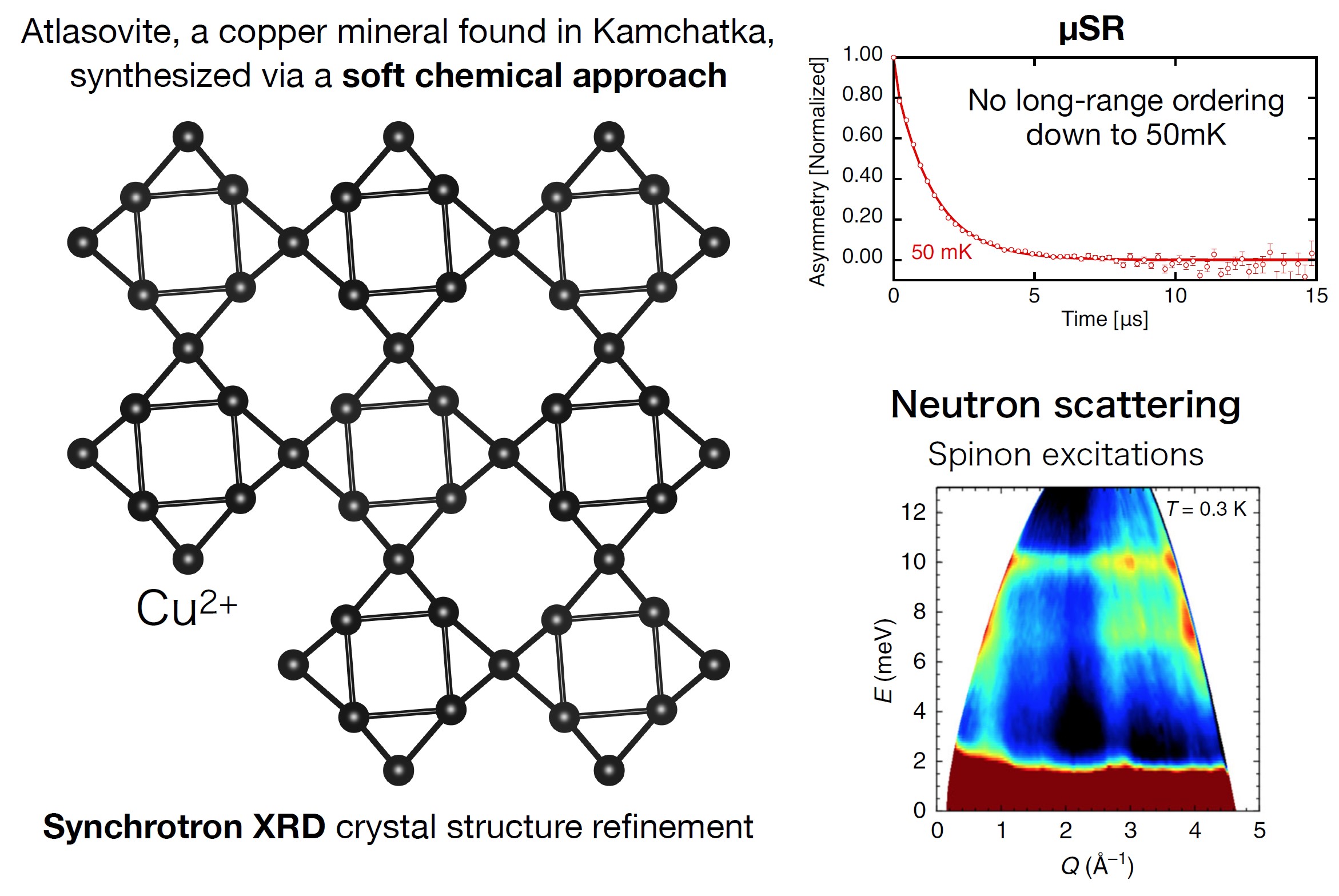
Observation of the Quantum Spin Liquid State in Novel Two-dimensional Material
We searched for compound with the square kagome lattice (SKL) containing S = 1/2 spins, and synthesized the first compound of a SKL antiferromagnet, atlasovite (KCu6AlBiO4(SO4)5Cl), successfully. Comprehensive experimental studies reveal the formation of a gapless quantum spin liquid state at very low temperatures close to the ground state.
M. Fujihala et al., Nat. Commun. 11, 3429 (2020).
Magnetic ground state in spin frustrated system AYb2S4(A=Cd,Mg)
By using muon spin rotation/relaxation technique(µSR), which is very sensitive to local electronic and spin state, we have clarified magnetic ground states in spin frustrate spinel type structural compounds, AYb2S4(A=Cd,Mg).
T.Higo et al., Phys. Rev. B 95, 174443 (2017).