Nuclear Mass
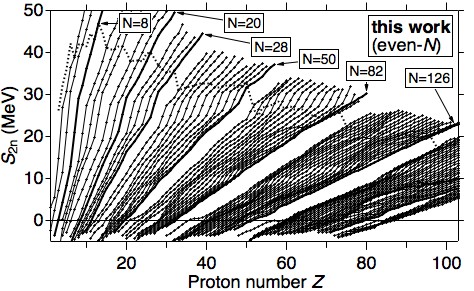
@Nuclear mass is a fundamental quantity in nucleus and equals to total energy of nuclei because of the equivalence of mass and energy, therefore determines the stability of nucleus, governs its decays, and influences the reaction.
Papers
- Nucl. Phys. A 671 (2000): Single-particle potentials for spherical nuclei
- Nucl. Phys. A 674 (2000): Nuclear Mass formula by a new method
- Prog. Theor. Phys. 113 (2005): Nuclidic Mass Formula on a Spherical Basis with an Improved Even-odd Term
- J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 82 (2013): Single-particle levels of spherical nuclei in the superheavy and extremely superheavy mass region
- Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 113D02 (2014): Estimating fission-barrier height by the spherical-basis method
Related Link
Applications
KTUY mass models is available to predict nuclear masses for extremely wider region. This result apply for varius kinds of decay for unkown nuclei and existence of nuclei:- Di-proton decay from ground-state 45 for the first time ( outside the proton drip line, referred as predicted Q2p valuej
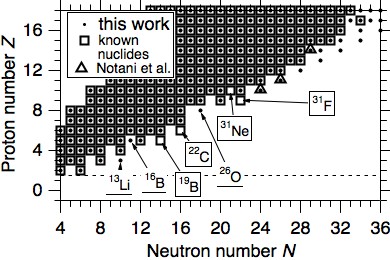
- Neutron drip line in the light neutron-rich mass regionPhysics, Viewpoint: A Walk Along the Dripline (2012),Physics, Viewpoint: Pushing Back the Frontier of Stability (2013)
- Lego 'Heisenberg' Valley', RIKEN Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based Science, 3D Chart of the nucldies, Niihama National College of Technology, Chart of the Nuclides
GOTO HOMEPAGE of Hiroyuki Koura