|
|
| Radiation emitted from radioactive materials (137Cs, 131I)) |
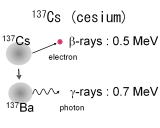 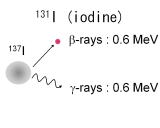 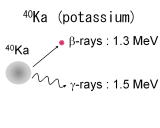
| Radioactive isotopes, 137Cs and 131I, are produced by fission reaction of uranium in an atomic reactor. On
the other hand, 40K nexsists in our body. Thus 40K is the major radiation source of internal exposure. These all isotopes
emit β-rays and γ-rays with the energy of 1 MeV or less. |
Effect of β-rays and γ-rays to DNA
γ-rays react with material through compton scattering. As the consequence
of this collision process, one electron so called compton electron (~MeV)
is ejected from the atom. This high energy electron induces DNA damage
with the similar process to those by β-rays. |
|

| Mean free path in living mater |
 |
Mean free path of β-rays and Compton electrons is about 1mm~1cm. Thus DNA
in a cell nu
Radioactive
Iisotopes |
Bq→Sv conversion factor
(1) |
Calculation condition
(2) |
Dose |
| 137Cs |
1.3x10E-8 |
300Bq/L (in water)
uptaking 1L per everday |
1400 μSv/year |
| 131I |
2.2×10-8 |
100Bq/L (in water)
uptaking 200mL milk
(a feeding bottle) |
18
μSv/year |
| 40K |
adult (normal condition) |
250
μSv/year
(3) |
(1) See recomendations in ICRP Publ.68(1994)or ICRP Publ.72(1996)
(2) Biological half period is not considered. In view of the life time
of 131I (8 days), it is assumed that initial radiation level of 131I is continued for 40 days before it loses all radioacivity. The integrated dose for 40 days are calculated.
(3) S. Kondo, Moleclular radiobiology, Japan Scientific Societies Press
(1972)(in Japanese.
|
 |
お知らせが入ります。 |
 |
お知らせが入ります。 |
|
|


